AI Automation for Business: How Intelligent Automation Transforms Operations

Across Europe and Japan, business leaders are navigating a period of operational complexity. Markets expect faster service, regulatory demands continue to tighten, and talent shortages intensify year after year. Many organizations still rely on fragmented processes, legacy systems, and labor-intensive workflows that no longer scale.
As a result, the conversation around automation has shifted. It is no longer about experimenting with AI; it is about building resilient, intelligent operations that remain compliant, efficient, and competitive.
However, there is still substantial confusion surrounding three commonly used terms: AI automation, intelligent automation, and intelligent process automation (IPA). While related, they represent different levels of automation maturity and deliver different types of business value. Choosing the wrong approach often leads to unnecessary complexity, limited ROI, or stalled transformation initiatives.
This article from The IT Source clarifies each concept, illustrates how enterprises apply them, and provides a structured roadmap for adopting automation in a way that is sustainable, secure, and aligned with regulatory expectations.
What Is AI Automation? (Foundation Layer)
AI automation refers to the use of artificial intelligence to perform tasks that typically require human interpretation or decision-making. Unlike traditional rule-based automation, AI can understand unstructured input such as emails, PDFs, screenshots, images, or chat messages, then act on that information with minimal intervention.
Common capabilities include reading and extracting data, recognizing patterns, making predictions, recommending actions, or executing tasks across systems. This makes AI automation particularly valuable for enterprises that depend on legacy platforms or have limited API availability, a common scenario in Japan and many European industries.
Organizational studies from the IBM Institute for Business Value indicate that organisations with mature intelligent IT automation report significantly reduced IT costs (up to 28%), lower downtime from cybersecurity incidents (up to 36%), and faster time-to-market.
AI automation serves as the foundation upon which more advanced automation layers are built. It is an accessible starting point that delivers measurable efficiency gains without requiring full process redesign.
What Is Intelligent Automation? (Orchestration Layer)
Intelligent automation expands beyond task execution. It orchestrates end-to-end workflows across different departments, systems, and human teams. In this layer, automation does not simply complete a task; it coordinates actions, escalates exceptions, manages approvals, and ensures that the right steps occur in the right sequence.
Intelligent automation typically combines:
- Artificial intelligence for understanding and decisioning
- Workflow automation tools for structuring multi-step processes
- Business rules to maintain consistency
- Human-in-the-loop mechanisms for sensitive or exceptional cases
To illustrate, consider a customer updating their delivery information. Intelligent automation can authenticate the user, validate the new address, update multiple systems (OMS, ERP, CRM), notify logistics partners, and alert human agents only when inconsistencies appear.
According to Gartner, hyperautomation is a business-driven, disciplined approach that organizations use to rapidly identify, vet, and automate as many business and IT processes as possible, using AI, machine learning, RPA, and other tools to orchestrate complex workflows at scale.
What Is Intelligent Process Automation (IPA)? (Process Transformation Layer)
Intelligent process automation (IPA) focuses on transforming core business processes that are structured, repeatable, and essential to enterprise operations. It integrates AI, workflow logic, validation rules, and system connectors to automate processes from end to end while ensuring governance, traceability, and compliance controls remain intact.
IPA is most valuable in functions where accuracy, consistency, and auditability are critical. This is why industries such as finance, logistics, e-commerce, telecommunications, and other regulated sectors adopt IPA to stabilize service quality and reduce operational risk.
Common IPA applications include:
- End-to-end invoice processing
- Anti–money laundering (AML) screening
- Cross-system order management
- Automated refund and claims handling
- Container tracking and ETA updates
- HR onboarding and compliance workflows
- Consolidated financial reporting
Rather than automating isolated tasks, IPA redesigns and standardizes entire processes. Insights from McKinsey highlight that when organizations combine AI with structured workflow redesign, they achieve significantly higher efficiency and fewer manual errors across operational processes not just cost savings, but improved reliability and governance.
What distinguishes IPA is the creation of a standardized, measurable, and auditable process that strengthens long-term scalability. Enterprises gain predictable outcomes, consistent service quality, and process integrity aligned with internal policies and external regulatory expectations.
Why These Three Layers Matter for Enterprise Strategy
Each automation layer solves a different class of problem.
AI automation reduces manual effort by handling tasks that were previously too complex for rule-based systems. It is a fast, low-risk way to eliminate repetitive work and improve accuracy.
Intelligent automation improves coordination, allowing enterprises to streamline workflows that involve multiple systems or human checkpoints. It focuses on service consistency, speed, and cross-departmental collaboration.
Intelligent process automation redesigns processes themselves, creating structured, governed workflows that meet high compliance and audit requirements.
Understanding these layers helps enterprises avoid misalignment between capability and expectation. Leaders can prioritize what the business needs now and build toward higher maturity without disrupting existing systems.
Enterprise Benefits: What Leaders Gain
Lower operational costs with greater efficiency
Automation directly offsets labor-intensive work, helping organizations scale operations without adding headcount. This is particularly relevant for markets like Japan, where workforce shortages and demographic pressures continue to grow.
Higher compliance and risk control
IPA ensures standardized data handling, clear audit trails, and documented workflows, supporting adherence to GDPR, the EU AI Act, and industry-specific regulatory frameworks.
Faster customer response and resolution
AI-powered agents and automated workflows provide immediate responses, multilingual support, consistent quality, and timely updates for service-related interactions. This leads to higher customer satisfaction and reduced backlog.
More accurate, real-time decision-making
Automation keeps enterprise data up-to-date. Leaders gain sharper visibility into performance metrics, operational bottlenecks, and risk indicators.
Compatibility with legacy environments
Many enterprises delay automation due to outdated systems. AI automation overcomes this barrier by interacting directly with interfaces, minimizing the need for costly system overhauls.
A Four-Stage Roadmap for Automation Success
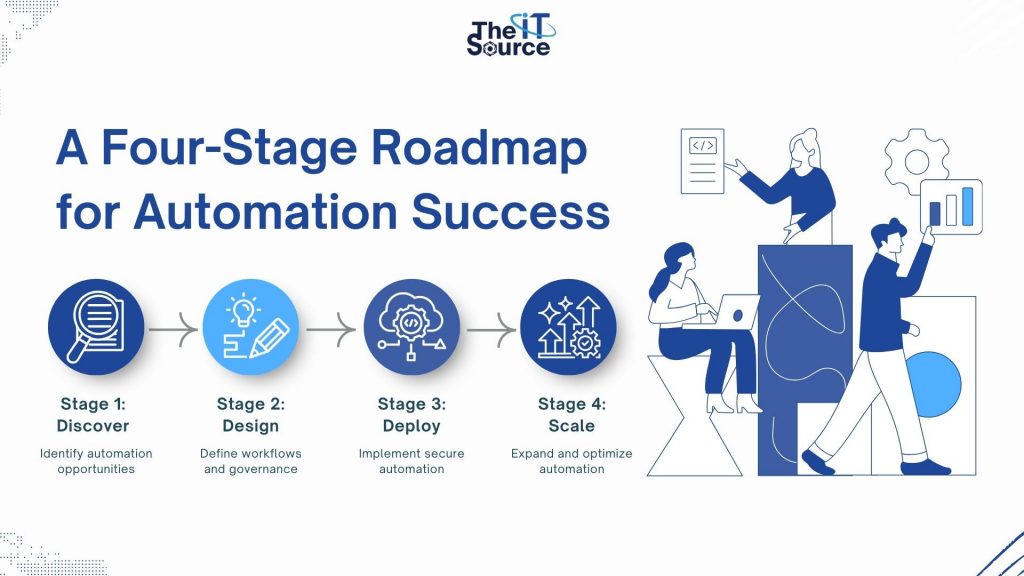
A structured roadmap helps enterprises adopt automation in a secure, scalable, and ROI-driven manner.
Stage 1: Discover
Organizations begin by identifying manual bottlenecks, process friction, and areas where automation would have the most impact. This prevents over-engineering and ensures alignment with business priorities.
Stage 2: Design
After selecting target processes, teams define workflow logic, determine how AI supports each step, map system integrations, and incorporate governance requirements.
Stage 3: Deploy
Automation solutions are implemented and integrated into enterprise systems such as CRM, ERP, and OMS. Deployment requires clear access controls, data-protection policies, audit logs, performance tests, and monitoring mechanisms. Regulated industries often opt for on-premise setups.
Stage 4: Scale
Once automation proves value, organizations expand across teams and processes. Scaling may involve introducing more complex workflows, adding predictive capabilities, or unifying automation under a broader operational framework.
This staged approach supports both short-term efficiency gains and long-term transformation.
Three Layers, One Strategic Direction
AI automation, intelligent automation, and intelligent process automation represent a progression of capabilities rather than separate technologies. Together, they form a strategic foundation for modern enterprise operations.
Organizations that understand these distinctions are better equipped to prioritize initiatives, manage risk, and build automation programs that deliver measurable business value. Whether the goal is reducing manual workload, improving compliance, strengthening service quality, or preparing for future AI adoption, the three layers work collectively to help enterprises operate with greater intelligence and resilience.
The IT Source supports enterprises across Europe and Japan with a structured approach to automation, covering everything from initial assessment to the deployment of AI Workers, AI Agents, and IPA frameworks designed to meet strict regulatory and operational requirements.
Contact The IT Source today to explore automation strategies tailored to your enterprise and industry.


